| CAS
NO. |
67-52-7 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
200-658-0 |
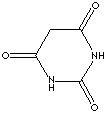
| FORMULA |
C4H4N2O3 |
| MOL
WT. |
128.09 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2933.52 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral rat LD50: >5000
mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
2,4,6- Trioxypyrimidine;
Pyrimidinetriol; N,N'-Malonylurea; |
| 2,4,6
(1H,3H,5H)-pyrimidinetrione;
2,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,3-diazine; Malonylurea; 2,4,6-Pyrimidinetriol;
2,4,6-Pyrimidinetrione; 2,4,6-Trihydroxypyrimidine;
2,4,6-Trioxohexahydropyrimidine; 6-Hydroxyuracil; 6-hydroxy-Hydrouracil;
|
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
250 - 255 C (Decomposws) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
142 g/l at
20 C |
| pH |
2 - 3 (50 g/l
Aq. solution) |
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. Decomposed if heated. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
Barbituric acid, chemically 2,4,6-trioxohexahydropyrimidine, a cyclic amide used as the parent compound
to produce barbiturates that act as central nervous system depressants. Like
malonic acid, barbituric acid has reactive hydrogen atom on the carbon alpha to
both carbonyl groups. Barbituric acid undergoes Knoevenagel condensation reaction
as a reactant to forms a large class of barbiturate
drugs that act as central
nervous system depressants. Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of a
reactive
hydrogen atom at 1,3-diketone compounds to a carbonyl
group, followed by an dehydration reaction. 1,3-Diketone compounds (beta-ketones)
include malonic
acid, diethyl malonate,
Meldrum's acid,
and acetoacetic acid derivatives. Barbituric acid itself does not give sedative and hypnotic effects but the
substituted derivatives with alkyl or aryl group at position 5 provide effects.
Thiobarbituric acid, replaced oxygen atom of the urea component by sulfur, the
parent compound of the thiobarbiturates which resembles the barbiturates in its
effects. Barbiturates are drugs that acts as sedative-hypnotic agents. The
short-acting barbiturates such as thiopental are used as intravenous
anesthetics. The long-acting barbiturate such as phenobarbital is an
anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy. They are used for the
suppression of anxiety, the induction of sleep, and the control of seizures.
Commercially available barbiturates are;
- Amobarbital
- Aprobarbital
- Butabarbital
- Butalbital
- Hexobarbital
- Mephobarbital
- Pentobarbital
- Phenobarbital
- Secobarbital
- Talbutal
- Thiobarbital
- Thiopental
Alternative medications, namely
benzodiazepines have replaced for barbiturates due to a high potential for
abuse.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
|
IDENTITY
(IR)
|
pass
|
|
PURITY
(G.C.)
|
99.0%
min
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
0.5%
max
|
|
MELTING
POINT
|
250 - 255 C |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/38-43, Safety
Phrases: 22-26-28 |
| PRICES |

|
